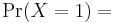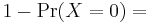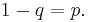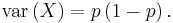Bernoulli distribution
In probability theory and statistics, the Bernoulli distribution, named after Swiss scientist Jacob Bernoulli, is a discrete probability distribution, which takes value 1 with success probability  and value 0 with failure probability
and value 0 with failure probability 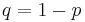 . So if X is a random variable with this distribution, we have:
. So if X is a random variable with this distribution, we have:
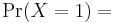
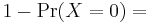
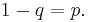
The probability mass function f of this distribution is
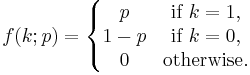
This can also be expressed as
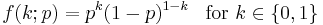 .
.
The expected value of a Bernoulli random variable X is 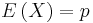 , and its variance is
, and its variance is
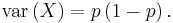
The kurtosis goes to infinity for high and low values of p, but for 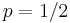 the Bernoulli distribution has a lower kurtosis than any other probability distribution, namely -2.
the Bernoulli distribution has a lower kurtosis than any other probability distribution, namely -2.
The Bernoulli distribution is a member of the exponential family.
Related distributions
- If
 are independent, identically distributed (i.i.d.) random variables, all Bernoulli distributed with success probability p, then
are independent, identically distributed (i.i.d.) random variables, all Bernoulli distributed with success probability p, then 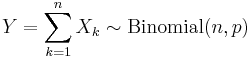 (binomial distribution).
(binomial distribution).
- The Categorical distribution is the generalization of the Bernoulli distribution for variables with any constant number of discrete values.
- The Beta distribution is the conjugate prior of the Bernoulli distribution.
- The Geometric distribution is the number of Bernoulli trials needed to get one success.
See also
- Bernoulli trial
- Bernoulli process
- Bernoulli sampling
- Binary entropy function
- Sample size
|
Probability distributions |
|
|
Discrete univariate with finite support |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Discrete univariate with infinite support |
|
Boltzmann · Conway–Maxwell–Poisson · discrete phase-type · extended negative binomial · Gauss–Kuzmin · geometric · logarithmic · negative binomial · parabolic fractal · Poisson · Skellam · Yule–Simon · zeta
|
|
|
|
Continuous univariate supported on a bounded interval, e.g. [0,1] |
|
Beta · Irwin–Hall · Kumaraswamy · logit-normal · raised cosine · triangular · U-quadratic · uniform · Wigner semicircle
|
|
|
|
Continuous univariate supported on a semi-infinite interval, usually [0,∞) |
|
Beta prime · Bose–Einstein · Burr · chi-square · chi · Coxian · Erlang · exponential · F · Fermi–Dirac · folded normal · Fréchet · Gamma · generalized extreme value · generalized inverse Gaussian · half-logistic · half-normal · Hotelling's T-square · hyper-exponential · hypoexponential · inverse chi-square (scaled inverse chi-square) · inverse Gaussian · inverse gamma · Lévy · log-normal · log-logistic · Maxwell–Boltzmann · Maxwell speed · Nakagami · noncentral chi-square · Pareto · phase-type · Rayleigh · relativistic Breit–Wigner · Rice · Rosin–Rammler · shifted Gompertz · truncated normal · type-2 Gumbel · Weibull · Wilks' lambda
|
|
|
|
Continuous univariate supported on the whole real line (−∞, ∞) |
|
Cauchy · extreme value · exponential power · Fisher's z · generalized normal · generalized hyperbolic · Gumbel · hyperbolic secant · Landau · Laplace · logistic · noncentral t · normal (Gaussian) · normal-inverse Gaussian · skew normal · slash · stable · Student's t · type-1 Gumbel · Variance-Gamma · Voigt
|
|
|
|
Multivariate (joint) |
|
Discrete: Ewens · multinomial · multivariate Polya · negative multinomial
Continuous: Dirichlet · Generalized Dirichlet · multivariate normal · multivariate Student · normal-scaled inverse gamma · normal-gamma
Matrix-valued: inverse-Wishart · matrix normal · Wishart
|
|
|
|
Directional, degenerate, and singular |
|
Directional:Circular Uniform · bivariate von Mises · Kent · univariate von Mises · von Mises–Fisher · Wrapped normal · Wrapped Cauchy · Wrapped Lévy
Degenerate: discrete degenerate · Dirac delta function
Singular: Cantor
|
|
|
|
Families |
|
|
Circular · compound Poisson · elliptical · exponential · natural exponential · location-scale · maximum entropy · mixture · Pearson · Tweedie
|
|
|
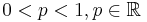
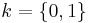
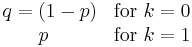
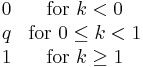
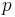
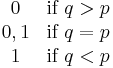
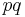
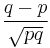
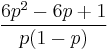
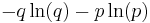
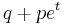
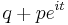
 and value 0 with failure probability
and value 0 with failure probability 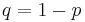 . So if X is a random variable with this distribution, we have:
. So if X is a random variable with this distribution, we have: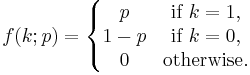
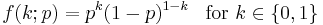 .
.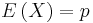 , and its variance is
, and its variance is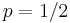 the Bernoulli distribution has a lower kurtosis than any other probability distribution, namely -2.
the Bernoulli distribution has a lower kurtosis than any other probability distribution, namely -2. are independent, identically distributed (i.i.d.) random variables, all Bernoulli distributed with success probability p, then
are independent, identically distributed (i.i.d.) random variables, all Bernoulli distributed with success probability p, then 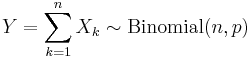 (binomial distribution).
(binomial distribution).